A Risk Assessment Method of LTE-R System Based on Improved Evidence Theory
-
摘要:
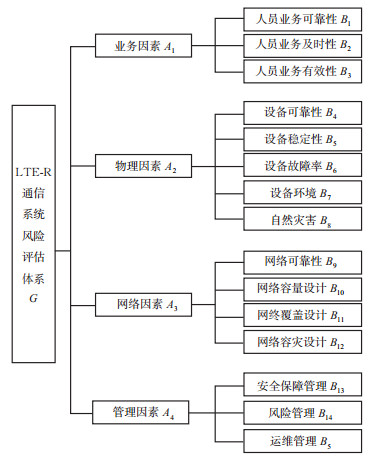
针对LTE-R通信系统运营安全风险评估中存在专家主观评判差异与冲突的问题,提出基于AHP与改进证据理论相结合的方法对LTE-R系统进行评估研究。利用模糊数学将专家模糊评语转化为定量隶属度表示,采用改进证据理论,基于皮尔逊系数改进克服证据间冲突的过程,通过加权分配证据可信度权值改善信息主观性,构造冲突因子修正证据融合过程,得到基本概率分配(BPA)函数矩阵。选取最大隶属度作为判断原则,评估相应系统的风险等级并与其他方法进行对比。结果表明:LTE-R系统实例分析评估结果为“可忽略风险”,置信度为83.41%,较折扣证据理论、灰色模糊综合安全评估法分别提升3.12%和16.95%,评估结果一致的前提下,改进的方法能改善专家评判冲突无法正确处理及融合问题,提供了高置信度风险等级值,为LTE-R系统的运营评估提供参考。
Abstract:A method based on AHP and improved evidence theory is proposed to evaluate LTE-R system, thus solving the problem of differences and conflicts of subjective evaluation of experts in operational security risk assessment of LTE-R system. Fuzzy mathematics is used to transform fuzzy evaluation of experts into quantitative membership degree. Adopting the improved evidence theory, the process of overcoming conflicts between evidences can be improved based on Pearson coefficient. Through the weighted distribution of evidence credibility weights, the subjectivity of information is improved. Conflict factors are constructed to modify the evidence fusion process, and the basic probability assignment(BPA)function matrix is finally obtained. The maximum membership degree is selected as a judgment principle to evaluate the risk level of the corresponding system, then compared with other methods. It can be summarized that the evaluation of the case analysis of the LTE-R system is "negligible risk" with a confidence level of 83.41%, which is 3.12% higher than the discount evidence theory, and 16.95% higher than the grey-fuzzy security assessment method. Under the premise of consistent evaluation results, the method can improve the problems of expert evaluation conflicts that cannot be handled correctly and integration, and provide a high-confidence risk level value, which provides a reference for the operation evaluation of the LTE-R system.
-
表 1 9元组模糊评语
Table 1. 9-tuple representation of fuzzy comments
μrkv1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 特差v1 1 0.8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 很差v2 0.2 1 0.8 0 0 0 0 0 0 差v3 0 0.2 1 0. 80 0 0 0 0 较差v4 0 0 0.2 1 0.8 0 0 0 0 一般v5 0 0 0 0. 51 0.5 0 0 0 较好v6 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 0.2 0 0 好v7 0 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 0.2 0 很好v8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 0.2 优秀v9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 表 2 9元组评语集
Table 2. 9-tuple representation of comment sets
μkRh 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 可忽略风险R1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 可接受风险R2 0 0 0 0 0 0.8 1 0.2 0 可容忍风险R3 0 0 0 0.2 1 0.2 0 0 0 不期望风险R4 0 0.2 1 0.8 0 0 0 0 0 不接受风险R5 1 0.8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 表 3 皮尔逊系数相关程度
Table 3. Correlation degree of Pearson coefficient
ρXY的范围 相关程度 0.00 ≤ ρXY<0.20 极弱相关或无关 0.20 ≤ ρXY<0.40 弱相关 0.40 ≤ ρXY<0.60 中等程度相关 0.60 ≤ ρXY<0.80 强相关 0.80 ≤ ρXY<1.00 极强相关 表 4 指标权重
Table 4. The weight of the indicator
二级指标 权重 B1 0.024 0 B2 0.055 0 B3 0.063 0 B4 0.225 1 B5 0.087 5 B6 0.079 2 B7 0.032 0 B8 0.020 9 B9 0.210 6 B10 0.078 1 B11 0.054 2 B12 0.022 2 B13 0.012 4 B14 0.005 0 B15 0.030 6 表 5 专家模糊评语表
Table 5. Fuzzy comment form of experts
指标层 专家1 专家2 专家3 专家4 专家5 专家6 专家7 专家8 专家9 专家10 B1 8 6 7 5 7 7 6 8 6 7 B2 6 7 8 8 7 7 7 6 7 6 B3 7 86 6 7 8 8 8 7 8 6 B4 7 9 9 7 9 9 8 9 9 9 B5 8 9 9 7 9 9 7 9 9 9 B6 9 9 9 6 9 8 9 9 7 9 B7 9 9 9 7 8 9 8 8 9 9 B8 7 7 9 6 8 9 8 9 7 9 B9 9 9 9 9 8 9 9 9 9 9 B10 6 9 7 8 9 9 9 9 8 9 B11 7 8 7 6 9 9 9 9 7 9 B12 9 9 7 8 9 9 9 8 7 7 B13 9 8 9 7 7 9 9 8 9 7 B14 7 8 9 8 9 9 6 8 7 9 B15 8 9 9 5 8 7 6 7 9 9 表 6 指标B6的BPA表
Table 6. BPA table for indicator B6
专家 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 1 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 2 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 3 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 4 0 0.444 4 0.555 6 0 0 5 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 6 0.517 2 0.482 8 0 0 0 7 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 8 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 9 0.063 0 0.881 9 0.055 1 0 0 10 0.947 3 0.052 7 0 0 0 表 7 风险因素BPA表
Table 7. BPA table of risk factors
风险因素 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 B1 0.011 0 0.929 3 0.059 7 0 0 B2 0.001 6 0.853 8 0.144 6 0 0 B3 0.164 1 0.769 3 0.066 6 0 0 B4 0.992 3 0.007 6 0.000 1 0 0 B5 0.993 0 0.006 9 0.000 1 0 0 B6 0.975 4 0.024 5 0.000 1 0 0 B7 0.936 5 0.063 4 0.000 1 0 0 B8 0.814 6 0.185 0 0.000 4 0 0 B9 0.996 3 0.003 7 0 0 0 B10 0.968 0 0.031 9 0.000 1 0 0 B11 0.895 8 0.103 9 0.000 3 0 0 B12 0.689 3 0.308 4 0.002 3 0 0 B13 0.649 3 0.350 3 0.000 4 0 0 B14 0.771 3 0.227 1 0.001 6 0 0 B15 0.904 9 0.091 6 0.003 6 0 0 -
[1] 杨晓燕. 发展下一代铁路移动通信系统的探讨[J]. 高速铁路技术, 2017, 8 (1): 54-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8247.2017.01.012YANG Xiaoyan. Discussion on the development of next generation railway mobile communication system[J]. High Speed Railway Technology, 2017, 8 (1): 54-56. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8247.2017.01.012 [2] CHEN Mengjia, ZHAO Yisheng, GAO Jincheng, et al. Adaptive modulation and frame length method based on Moore state machine in LTE-R communication system[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14 (8): 1327-1334. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.5835 [3] 杨树忠, 马良德, 杨吉, 等. 铁路下一代移动通信系统LTE-R检测技术研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2018, 667 (1): 70-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLZG201801014.htmYANG Shuzhong, MA Liangde, YANG Ji, et al. Research on LTE-R Detection technology of railway next generation mobile communication system[J]. China Railway, 2018, 667(1): 70-73. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLZG201801014.htm [4] 李春铎. 铁路LTE-R宽带移动通信系统高速适应性研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2019.LI Chunduo. Research on high speed adaptability of railway LTE-R broadband mobile communication system[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Railway Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese) [5] 腾辉. LTE-R通信系统安全设计与评估技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2012.TENG Hui. Research on security design and evaluation technology of LT-R communication system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese) [6] 高志远. LTE-R通信系统可靠性分析与研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016.GAO Zhiyuan. Reliability analysis and research of LTE-R communication system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese) [7] 陈永刚, 周净毓, 戴乾军, 等. 基于组合赋权-云模型的LTE-R系统的安全评估研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2019, 16 (12): 3110-3118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201912026.htmCHEN Yonggang, ZHOU Jingyu, DAI Qianjun, et al. Research on security assessment of LTE-R systems based on combined empowerment-cloud model[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16 (12): 3110-3118. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201912026.htm [8] 虎丽丽, 徐岩, 陶慧青. 基于动态故障树的LTE-R通信系统可靠性分析[J]. 计算机工程, 2020, 46 (9): 205-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC202009028.htmHU Lili, XU Yan, TAO Huiqing. Reliability analysisLTE-R communication system based on dynamic fault tree[J]. Computer Engineering, 2020, 46 (9): 205-212. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC202009028.htm [9] 向志华. 朔黄重载铁路TD-LTE系统QoS评价标准研究[J]. 高速铁路技术, 2016, 7 (3): 7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8247.2016.03.002XIANG Zhihua. Research on QoS evaluation standard of TD-LTE system of Shuohuang heavy-haul railway[J]. High Speed Railway Technology, 2016, 7(3): 7-10. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8247.2016.03.002 [10] 马迪迪. 基于高速铁路LTE-R通信系统安全风险评估技术研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2019.MA Didi. Research on safety risk assessment technology based on high-speed railway LTE-R communication system[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese) [11] 张栋, 庄其建, 赖理文. 基于AHP和熵权法的地铁车站深基坑施工安全评价[J]. 现代交通技术, 2016, 13 (3): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9889.2016.03.022ZHANG Dong, ZHUANG Qijian, LAI Liwen. Safety evaluation of deep foundation pit construction of subway station based on AHP and entropy weight method[J]. Modern Transportation Technology, 2016, 13 (3): 80-86. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9889.2016.03.022 [12] CHEN Luyuan, DENG Xinyang. A modified method for evaluating sustainable transport solutions based on AHP and Dempster-Shafer evidence theory[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(4): 563-580. doi: 10.3390/app8040563 [13] SILVA M M, HIPEL K W, KILGOUR D M, et al. Strategic analysis of a regulatory conflict using Dempster Shafer theory and AHP for preference elicitation[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering, 2019, 28 (4): 415-433. doi: 10.1007/s11518-019-5420-1 [14] GHOSH R, KUMAR P, ROY PP. A Dempster-Shafer theory based classifier combination for online Signature recognition and verification systems[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2019, 10 (9): 2467-2482. doi: 10.1007/s13042-018-0883-9 [15] 宗芳, 于萍, 吴挺, 等. 常规公交风险的SEM与Bayesian Network组合评估方法研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2018, 36 (4): 22-28. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2018.04.004ZONG Fang, YU Ping, WU Ting, et al. Research on the combined evaluation method of SEM and Bayesian network for conventional bus risk[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2018, 36 (4): 22-28. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2018.04.004 [16] 张友鹏, 王亚惠, 杨妮. 基于折扣证据理论的应答器系统风险评估[J]. 铁道科学与工程报, 2017, 14 (9): 1990-1997. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201709025.htmZHANG Youpeng, WANG Yahui, YANG Ni. Risk assessment of transponder system based on discount evidence theory[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2017, 14(9): 1990-1997. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201709025.htm [17] LI Rongfei, CHEN Zhiyuan, LI Hao, et al. A new distance-based total uncertainty measure in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 1 (2): 1-29. [18] 毛一凡, 张多林, 王璐. 基于重合度的证据冲突度量方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32 (2): 293-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201702014.htmMAO Yifan, ZHANG Duolin, WANG Lu. Evidence conflict measurement method based on coincidence degree[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32 (2): 293-298. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201702014.htm [19] ADANE D, KHANUJA H K. Monitor and detect suspicious transactions with database forensics and Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence[J]. International Journal of Electronic Security and Digital Forensics, 2020, 12 (2): 154-159. doi: 10.1504/IJESDF.2020.106302 -




 下载:
下载: