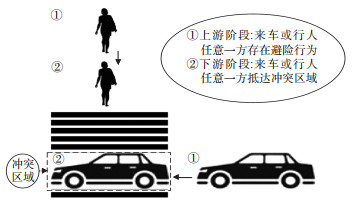
A Model of Risk Classification and Forewarning for Pedestrian Crossing Behavior at Unsignalized Urban Roadways
-
摘要: 为量化城市无信号控制路段下的行人过街风险,避免人车冲突事故频发,提出基于K-means算法的行人过街风险量化分级方法,并在此基础上建立了基于随机森林的行人过街风险分级预警模型。考虑时空接近程度及潜在碰撞伤害大小,选取冲突时间差、潜在碰撞距离与潜在碰撞能量3个指标,准确刻画出实际的人车交互场景,并利用K-means算法对行人过街风险状态进聚类划分,明确相应的行人过街风险等级。综合行人过街场景中包含的天气状况、道路交通设施、行人交通特征、机动车交通特征与历史事故等5类风险隐患因素,提出了30项行人过街风险二级指标,依据基尼不纯度对风险指标进行筛选并构建出最优的预警指标集,以此为模型输入,利用随机森林算法建立了能对行人过街风险进行细化、量化预测的分级预警模型。以山西省某市3处行人过街样本数据为算例验证模型的可行性。算例分析表明:行人过街风险等级分为5级时,量化分级结果能与实际行人过街情景较好吻合;本文提出的分级预警模型对各风险等级预测的整体正确率可达86.67%,其中对一级与四级风险的预警能力最为突出,一级风险识别准确率达到100%,四级风险识别准确率达到94.7%。本研究提出的行人过街风险分级预警模型解决了既往研究中存在的风险指标不够全面、风险等级划分未完全贴合实际场景、预警等级未细化等问题,提高了风险预警准确率。Abstract: To quantify the collision risk for pedestrian crossing at unsignalized urban roadways, a method for classifying such risk is proposed based on a K-means algorithm, and a forewarning model is also developed based on random forest technique. Three indicators, conflict time difference to conflict, potential collision distance, and potential collision energy, are selected to describe the real-world human-vehicle interactions by considering their temporal and spatial proximity and the severity of potential collisions. A K-means algorithm is applied to cluster the states of pedestrian crossing risk and classify the corresponding risk into different levels. Thirty indicators are proposed by analyzing the potential risk factors from the following five aspects, including weather, traffic facilities, behaviors of traffic participants, historical accidents, and others presented in the process of pedestrian crossing. An optimal set of forewarning indicators is extracted after screening the above indicators according to the Gini purity. Taking the optimal set as the model input, a hierarchical forewarning model which can refine and predict the pedestrian crossing risk is developed by using a random forest algorithm. The accuracy of the model is verified based on three pedestrian crossing datasets collected in a city of Shanxi Province. Experiment results show that quantitative classification is consistent with the real-world pedestrian crossing scenarios when the level of pedestrian crossing risk is divided into 5 levels. The overall accuracy of the hierarchical forewarning model reaches 86.67%. The accuracy of identifying level Ⅰ and level Ⅳ risk are even higher, as their accuracy reaches 100% and 94.7%, respectively. The proposed method also mitigates several issues from the models presented in the previous studies, such as incomplete risk indicators, unrealistic risk classification and unrefined warning level, and improves the accuracy of risk forewarning for pedestrians crossing streets.
-
表 1 天气状况输入特征
Table 1. Input feature of weather
一级变量 二级变量 变量类型 单位或取值 天气状况XA 天气XAa 分类变量 晴=0、雨=1、雪=2、霜冻=3、多云=4 白昼XAb 分类变量 凌晨=0、正午=1、傍晚=2、夜晚=3 气温XAc 连续变量 ℃ 风速XAd 连续变量 m/s 表 2 道路交通设施输入特征
Table 2. Input feature of road traffic facilities
一级变量 二级变量 变量类型 单位或取值 道路交通设施XB 有无行人过街标志XBa 分类变量 是=1,否=0 有无违法抓拍设施XBb 分类变量 是=1,否=0 有无行人过街预警设施XBc 分类变量 是=1,否=0 有无二次过街设施XBd 分类变量 是=1,否=0 来车方向上游交叉口是否信号控制XBe 分类变量 是=1,否=0 来车方向上游交叉口信号周期长度XBf 连续变量 s 机动车停止线距人行横道距离XBg 连续变量 m 机动车车道宽度XBh 连续变量 m 机动车车道数量XBi 离散变量 从1开始的自然数 人行横道宽度XBj 连续变量 m 人行横道长度XBk 连续变量 m 表 3 行人交通特征输入特征
Table 3. Input feature of pedestrian traffic characteristics
一级变量 二级变量 变量类型 单位或取值 行人交通特征XC 冲突发生前的的步速XCa 连续变量 m/s 冲突瞬间距冲突区域距离XCb 连续变量 m 过街集群人数XCc 离散变量 从1开始的自然数 过街行为倾向XCd 分类变量 减速后退=0,停止=1,加速穿越=2 性别XCe 分类变量 女=0,男=1 年龄段XCf 分类变量 青少年=0,中年=1,老年=2 行人着装类型XCg 分类变量 亮色系=0,暗色系=1 过街行人流量XCh 离散变量 人/h 表 4 机动车交通特征输入特征
Table 4. Input feature of Motor vehicle traffic characteristics
一级变量 二级变量 变量类型 单位或取值 车型XDa 分类变量 小型车=0,中型车=1,大型车=2 冲突发生前的车速XDb 连续变量 km/h 机动车交通特征XD 冲突瞬间距冲突区域距离XDc 连续变量 m 车流量XDd 离散变量 veh/h 车头时距XDe 连续变量 s 注:“车头时距”为来车方向距离过街行人最近的车与前车的车头时距;“车型”“车速”分别为来车方向距离过街行人最近的车所对应的“车型”“车速”。 表 5 历史事故情况输入特征
Table 5. Input feature of historical traffic accidents
一级变量 二级变量 变量类型 单位 事故类型XE 统计1年内的行人与机动车间的事故次数XEa 离散变量 起 统计1年内的机动车与机动车间的事故次数XEb 离散变量 起 表 6 调查详情
Table 6. Details of survey
地点 时间段 天气 停止线距离人行横道距离/m 有无行人过街标志 人行横道宽度/m 样本数量/个 新建东街中国人民银行东北侧40 m人行横道 夜晚 晴 5 无 5 45 新建东街灵石三中南门人行横道 正午 多云 3 有 5 209 新建东街烟草专卖局北门人行横道 傍晚 多云 3 无 4 61 表 7 行人过街风险级别
Table 7. Pedestrian crossing risk levels
风险等级 风险等级量化指标 过街情景 1级 EPCE值大,LPCD与TCTD值小 来车先行通过冲突区域,没有明显减速,行人近距离等待过街,此类情景下风险最大,对应图 2(f)中☆形样本点 2级 EPCE值大,LPCD值小,TCTD值偏大 来车先行通过冲突区域,没有明显减速,行人等待过街,与来车间距相对较远,对应图 2(f)中□形样本点 3级 EPCE值大,LPCD值偏小,TCTD值大 行人先行通过冲突区域,来车距离较远但车速快,行人容易判断失误,对应图 2(f)中*形样本点 4级 EPCE值小,LPCD与TCTD值均偏小 行人先行通过冲突区域,来车多减速或停车让行,对应图 4(f)中○形样本点。 5级 EPCE值偏小,LPCD值大,TCTD值大 行人先行通过冲突区域,来车距离远且车速慢,此类情景下风险最小,对应图 2(f)中△形样本点 表 8 各组预警输入特征集的Ac
Table 8. Accuracy rate of each early warning input feature set
组号 预警输入特征 AC/% 1 XCa 71.67 2 XCa, XDc 80.00 3 XCa, XDc, XDb 76.67 4 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb 83.33 5 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd 85.00 6 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb 83.00 7 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa 76.67 8 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf 73.33 9 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa 68.33 10 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa, XCg 80.00 11 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa, XCg, XBa 71.67 12 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa, XCg, XBa, XBj 75.00 13 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa, XCg, XBa, XBj, XCe 71.67 14 XCa, XDc, XDb, XCb, XCd, XAb, XAa, XCf, XDa, XCg, XBa, XBj, XCe, XBg 75.00 -
[1] 公安部道路交通安全研究中心. 中国大城市道路交通发展研究报告(2020)[R]. 北京: 公安部道路交通安全研究中心, 2021.Research Institute for RoadSafety of MPS. Rsearchreport on metropolis'road traffic development in China(2020)[R]. Beijing: Research Institute for Road Safety of MPS, 2021. (in Chinese) [2] HERNANDEZ D C, FILONENKO A, HARIYONO J, et al. Laser based collision warning system for high conflict vehicle-pedestrian zones[C]. 2016 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics(ISIE), Santa Clara, USA: IEEE, 2016. [3] 胡鹏程, 张超, 鲍丙计, 等. 基于车载视频的行人预警系统[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2016(11): 43-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2016.11.008HU P C, ZHANG C, BAO B J, et al. Pedestrian warning system based on on-board videos[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2016(11): 43-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2016.11.008 [4] 彭金栓, 张磊, 徐磊, 等. 基于行人动作预判的碰撞预警系统: 201810276866. 3[P]. 2018-03-30.PENG J S, ZHANG L, XU L, et al. Collision early warning system based on pedestrian action prediction: 201810276866. 3[P]. 2018-03-30. (in Chinese) [5] 赵彬. 面向车载行人预警系统需求的行人过街意图识别模型研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021.ZHAO B. Research on pedestrian crossing intention recognition model facing the demand of vehicle-mounted pedestrian warningsystem[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2021. (in Chinese) [6] MOGELMOSE A, TRIVEDI M, MOESLUND T B. Trajectory analysis and prediction for improved pedestrian safety: Integrated framework and evaluations[C]. 2015 IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium(Ⅳ), Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2015. [7] LEWIN I, O'FARRELL J. Development and analysis of a pedestrian crossing warning system[J]. Journal of the Illuminating Engineering Society, 2000, 29(2): 100-105. doi: 10.1080/00994480.2000.10748322 [8] SISIOPIKU V P, ELLIOTT J R. Active warning systems: Synthesis[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2005, 131(3): 205-210. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2005)131:3(205) [9] HOYE A, LAURESHYN A. SeeMe at the crosswalk: Be-fore-after study of a pedestrian crosswalk warning system[J]. Transportation research part F: traffic psychology and behaviour, 2019(60): 723-733. [10] 刘佳丽, 黄世震, 何恩德. 基于ARM和深度学习的智能行人预警系统[J]. 信息技术与网络安全, 2021, 40(12): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXJY202112010.htmLIU J L, HUANG S Z, HE E D. Intelligent pedestrian warning system based on ARM and deep learning[J]. Information Technology and Network Security, 2021, 40(12): 60-64. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXJY202112010.htm [11] 陈一锴, 胡晶, 李健昌, 等. 1种基于手机APP的行人过街预警系统: 201811490019. 3[P]. 2018-12-06.CHEN Y K, HU J, LI J C, et al. A pedestrian crossing warning system based on mobile phone APP: 201811490019. 3[P]. 2018-12-06. (in Chinese) [12] 吴宇通, 张洪昌, 曾娟. 基于车联网的车辆与行人碰撞预警方法研究[J]. 科技与创新, 2020(17): 1-3.WU Y C, ZHANG H C, ZENG J. Early warning method of vehicle pedestrian collision based on Internet of vehicles[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2020(17): 1-3. (in Chinese) [13] 裴玉龙, 冯树民. 基于交通冲突的行人过街危险度研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2007, 39(2): 285-287. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2007.02.029PEI Y L, FENG S M. Study on hazard degree of pedestrians'crossing based on traffic conflict[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007, 39(2): 285-287. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2007.02.029 [14] 项乔君, 卢川, 吴群, 等. 基于冲突严重性划分的公路平交口安全评价[J]. 公路交通科技, 2008, 25(8): 128-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK200808027.htmXIANG Q J, LU C, WU Q, et al. Traffic safety evaluation on highway intersection based on severity division of traffic conflict[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2008, 25(8): 128-131. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK200808027.htm [15] 孙林. 基于交通冲突技术的城市交叉口交通安全评价方法研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015.SUN L. Study on evaluation method of urbanintersection traffic safety on traffic conflict technique[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015. (in Chinese) [16] 向红艳, 张清泉. 无信号控制路段行人过街风险分析模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(4): 126-130.XIANG H Y, ZHANG Q Q. Model for evaluating risk of pedestrian in crossing unsignalizedroad[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(4): 126-130. (in Chinese) [17] 袁泉, 晏楠飞, 郝威. 基于心理安全距离的行人风险评价及预警算法研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(1): 109-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202201010.htmYUAN Q, YAN N F, HAO W. Pedestrian risk assessment and early warning algorithm based on psychological safety distance[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(1): 109-118. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202201010.htm [18] 余昕宇. 基于人因分析的无信控过街风险评估及安全改善研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2020.YU X Y. Research on risk evaluation and safety improvement of unsignalized crossing sections based on human factor analysis[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [19] 袁黎, 何娟, 蔡明杰, 等. 基于安全熵的信号控制路段行人过街风险评估模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(8): 25-30.YUAN L, HE J, CAI M J, et al. Model forevaluating risk of pedestrian in crossing signalized section based on safety entropy[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(8): 25-30. (in Chinese) [20] KADALI B R, VEDAGIRI P. Proactive pedestrian safety evaluation at unprotected mid-block crosswalk locations under mixed traffic conditions[J]. Safety Science, 2016(89): 94-105. [21] ZHANG C B, CHEN F, WEI Y Wei. Evaluation of pedestrian crossing behavior and safety at uncontrolled mid-block crosswalks with different numbers of lanes in China[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019(123): 263-273. [22] 周扬, 付锐, 袁伟, 等. 驾驶人认知分心识别随机森林模型研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(1): 20-25.ZHOU Y, FU R, YUAN W, et al. Researchon drivers cognitive distracted recognition model based on random forest[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(1): 20-25. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: